Good science is good observation. Clinical features basically refer to the observations of a disease process by the treating physician. This comprises of the various signs and symptoms of a disease. It is important to understand the Embryology (development) and Epidemiology (statistical numbers).
Embryology of ROP :
1. Blood vessels start to migrate from the optic disc to the Ora Serrata (edge of the retina) at about 16 weeks
2. The transformation of precursor mesenchymal spindle cells into capillary networks are termed as Vasculogenesis
3. Further maturation leads to angiogenesis and from here on out, the mature vessels extend to the nasal ora serrata by 36 weeks, followed by temporal ora by 39 - 41 weeks
All these statements are only indicative and are presented to give a general idea of the time line and degree of risk and are not absolute
Risk Factors of Retinopathy of Prematurity:
- Prematurity
- Ventilator support
- Low Birth Weight
- Cardiac Defects
- Other Infections
- History of blood transfusions
- Need for surfactant
- Multiple pregnancy (twins/ triplets)
- Maternal risk factors
- Intrauterine growth restriction/retardation
- Abnormal doppler changes
Epidemiology (basic statistics):
- 65.8% of infants <1250 g developed ROP but only 6% reached the threshold for treatment
- No gender association
- African American children are less susceptible
- Multiple births lead to increased risks
- Incidence and severity closely correlates with low birth weight (LBW) and
-
earlier gestational age
- >80% in infants <28 weeks
- >60% in infants 28 – 31 weeks
-
Timing of pathological vascular events correlated more closely with post
conception age than chronological age, independent of birth weight
- - Median age of onset of stage 1 ROP was 34 weeks after conception
- - 37 Weeks is the median onset for threshold disease
All these statements are only indicative and are presented to give a general idea of the time line and degree of risk and are not absolute.
Classifications of Clinical Features in Retinopathy of Prematurity
The major clinical features are differentiated into three segments. They are,
- Zone – Based on the location
- Stage – Based on Disease Severity
- Vascular attribute in the posterior pole – plus or pre-plus
Diagnosis of ROP should mention all these attributes.
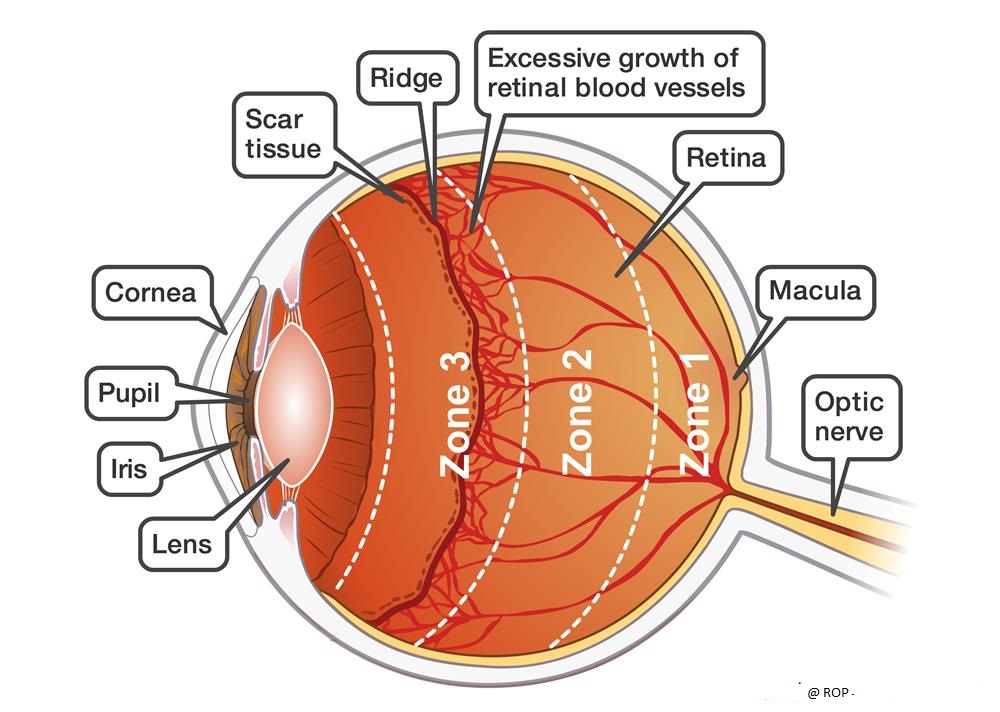
Zone (Location):
Based on the location of occurrence, ROP is classified into three zones. The development of retinal vasculature to Ora Serrata starts from the optic nerve head and so these zones are centered on the optic disc.
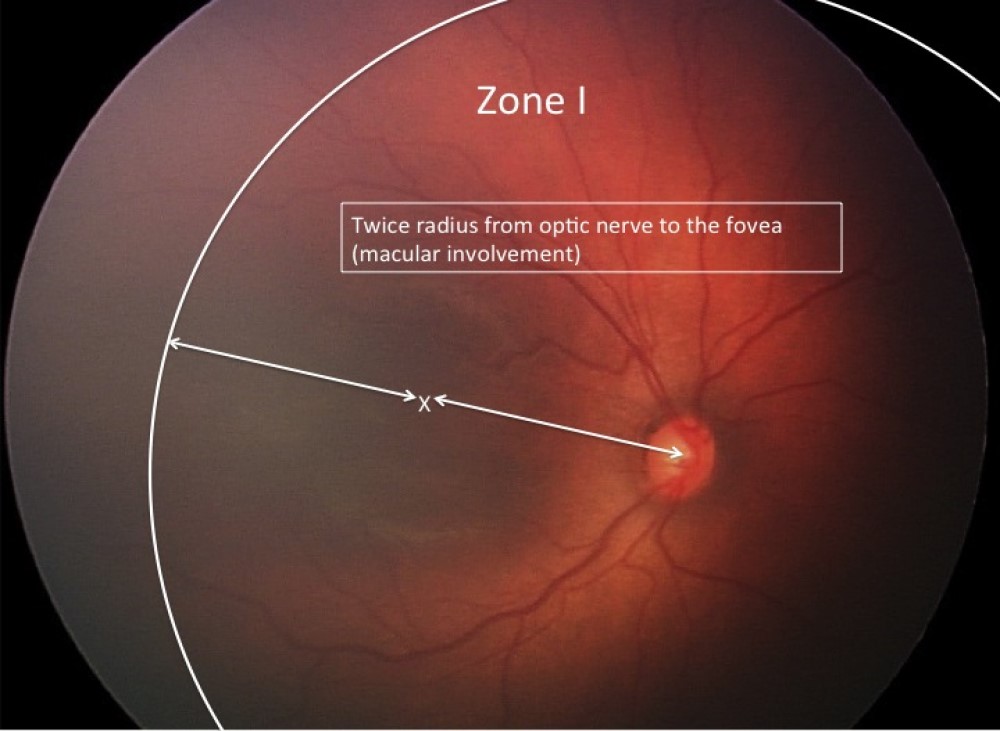
Zone I :
This area is generally referred to as the area contained within a circle whose centre is center of the optic nerve head (optic disc) having a radius of twice the distance from the center of the optic nerve to the macula center.
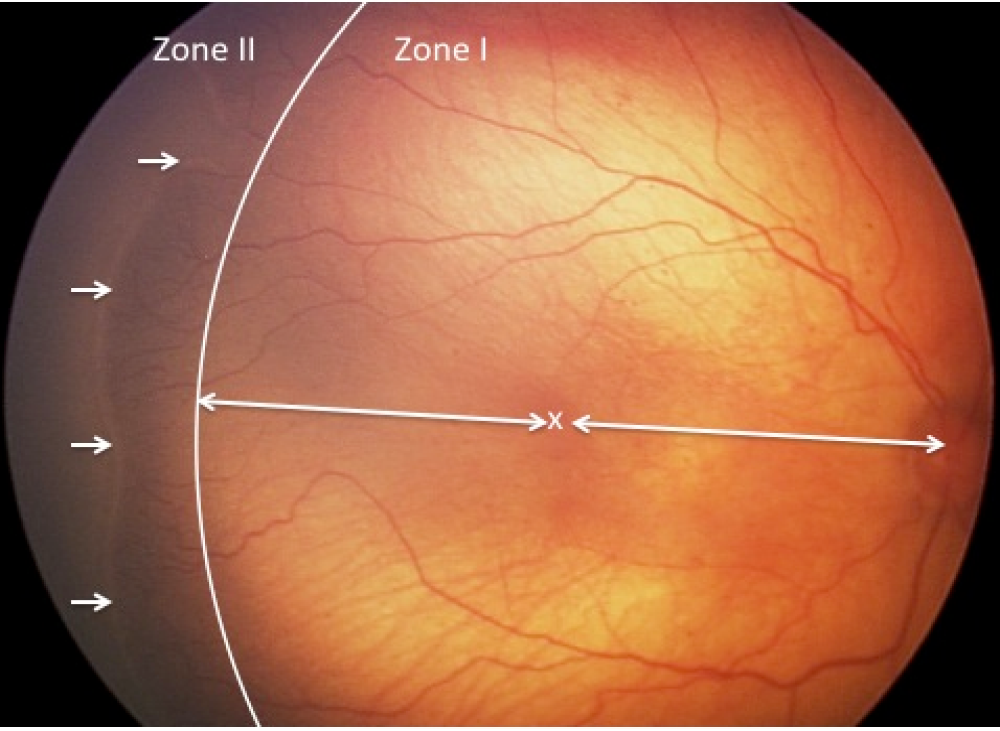
Zone II :
The area around Zone I circle centrifugally with a radius that is equal to the distance between nasal ora serrata to the center of the optic disc.
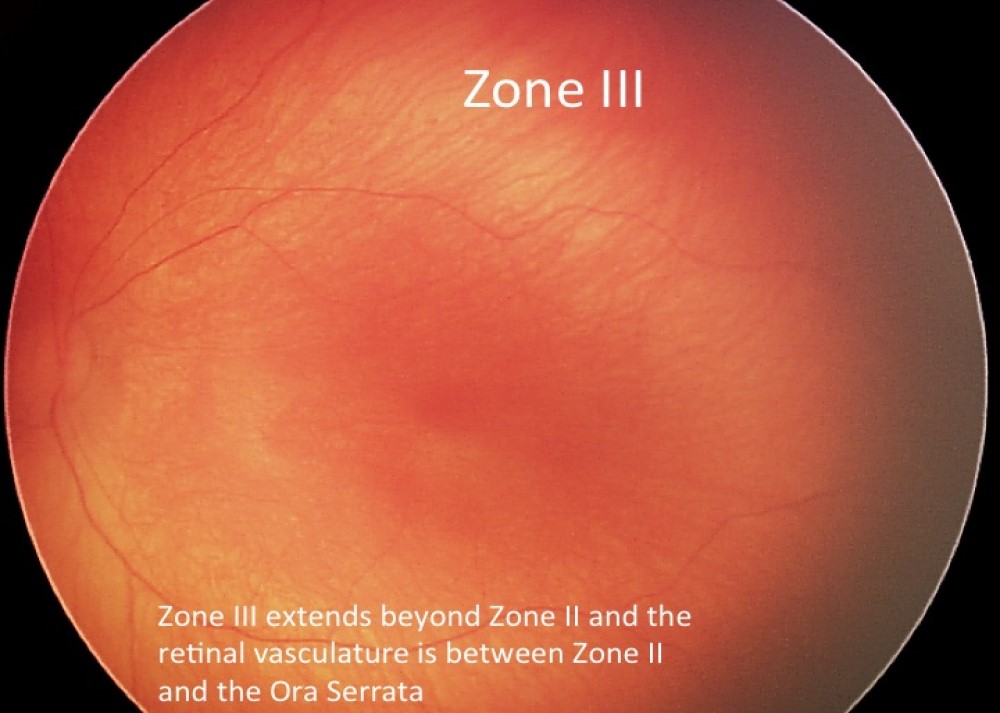
Zone III :
The temporal retinal expanse beyond Zone II is Zone III. Anyhow, both Zone II and Zone III are always mutually exclusive.
Stage (Disease Severity)
In premature or preterm infants, the growth of the blood vessels that stream over the Retinal surface is incomplete. This incomplete vascularisation is mapped as Stage 0.
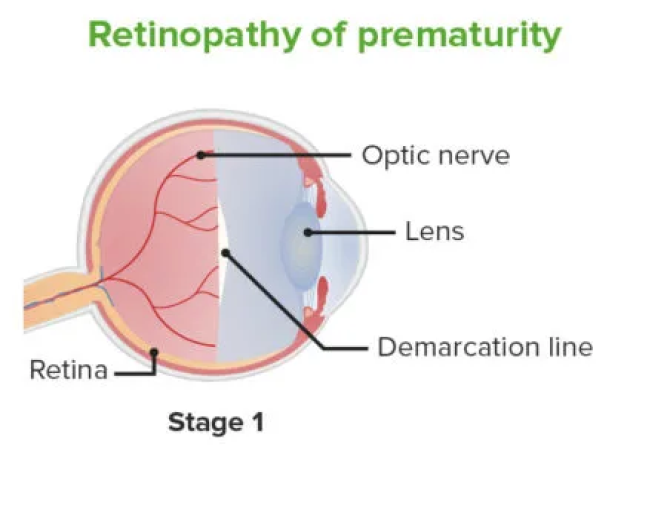
This line appears as thin and basically flat line over the retinal surface. It divides the anterior avascular retina from the posterior vascular retina. Would like to consider this as a single dimension where length is of primary focus and importance and also its relative presence from the ora.
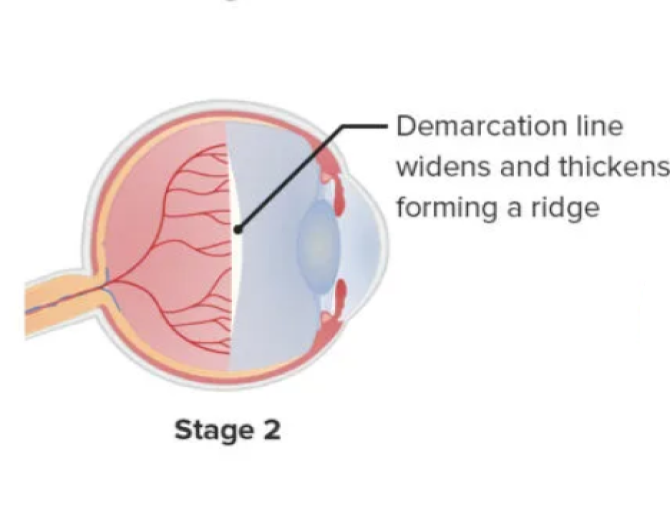
This starts from the demarcation line and extends over the retinal surface giving a bit of breadth. The ridge tends to switch from white to pink color. Popcorns like lesions that appear on the posterior aspect of the ridge could be considered as precursors for fibrovascular growth. They are basically a small outlying clump of neovascular tissue. This is an essential condition for stage 3. We could consider this effect as a two-dimensional lesion where there is length as well as width.
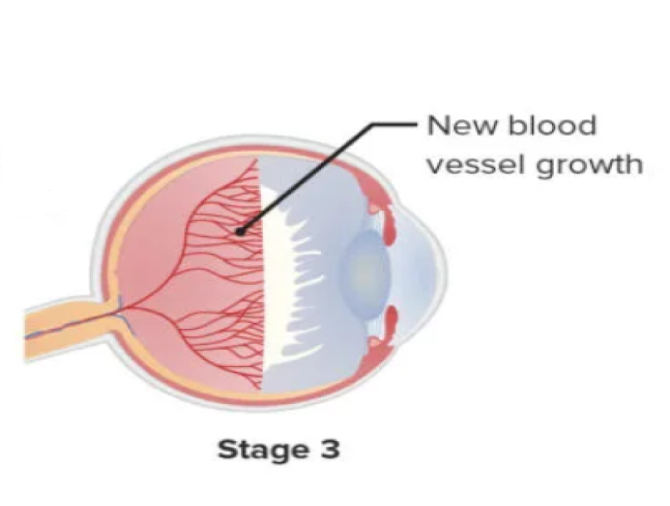
Neovascularization moves towards the vitreous from the ridge (takes off from the retinal surface). The extraretinal fibrovascular proliferating tissue is usually present at the posterior aspect of the ridge. These abnormal blood vessels are more fragile as they are cluster like and aren’t supported by the retinal surface. This stage can be considered as three dimensional as there is an element of height as well. This stage is crucial as it is when the treating physician is likely to perform laser treatment of the retina or administer anti VEGF injections.
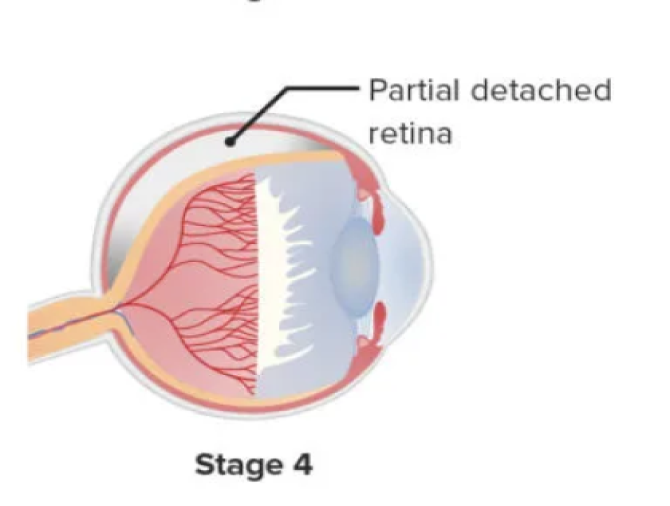
This stage is classified into two phases.
• Extrafoveal (stage 4A)
• Foveal (stage 4B)
Stage 4 has partial retinal detachments, which are always concave and most are circumferentially aligned. The retinal detachments begin at the point where the fibrovascular and vascularized retina is attached. The extension of retinal detachment depends on the quantity of neovascularization present
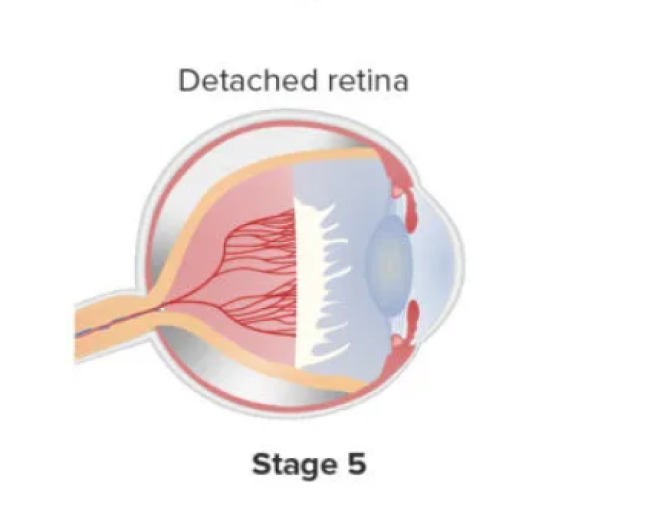
In this stage the retina will be totally detached from its wall. Retinal detachments are normally funnel shaped. The arrangement of the funnel further divides the stage depending on anterior and posterior portions as “open or narrowed”.
Vascular characteristics in the posterior pole :
The vascular attribute has been sub-classified into three phases. They are :
• Plus Disease
• Pre-Plus Disease
• Aggressive Posterior ROP
Plus disease
This feature when present hikes up the severity and risk. The following represents signs of plus disease :
- Iris vascular congestion
- Poor Pupillary dilation
- Vitreous haze
- Tortuous posterior retinal blood vessels
It should be mandatory to examine all infants with suspected ROP including those with poor dilation of pupils.
Few clinical trials have suggested a “standard” photograph to define the minimum amount of vascular inflammation and distortion. It should be present in a minimum of 2 quadrants to be diagnosed as plus disease. Advanced trials and researches are being conducted with contact cameras to standardize of plus disease using machine based studies.
Pre-Plus disease
Pre-plus disease is termed as vascular abnormalities of the posterior pole which are insufficient for the diagnosis of plus disease. This demonstrates more arterial distortion and dilatation than normal.
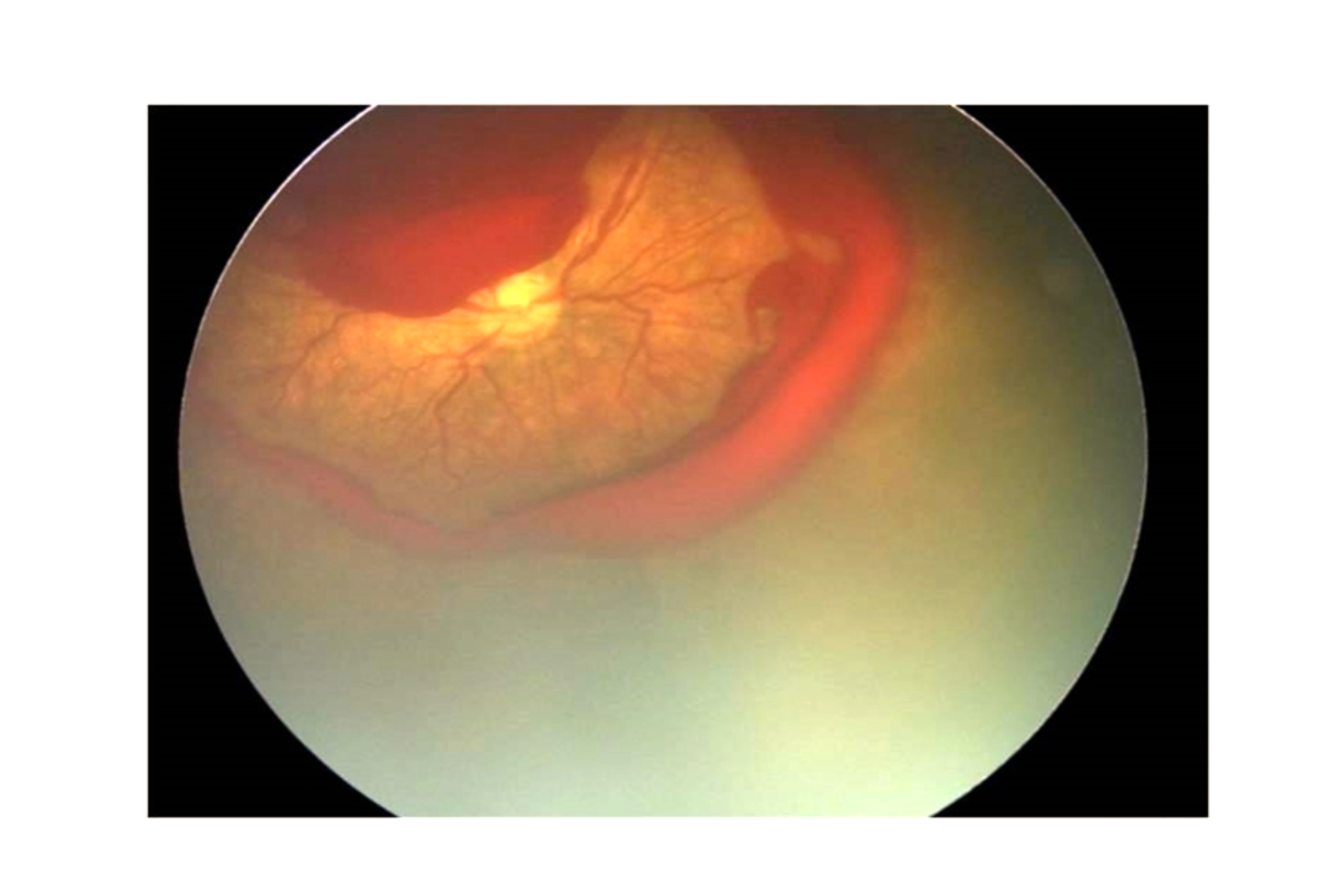
Aggressive Posterior ROP (AP-ROP)
Characteristic features of AP-ROP:
Aggressive ROP will progress to stage 5 if untreated. This is also known as “Rush Disease”; as it progresses rapidly. There are vascular curves and no clear demarcation line or ridge. Fundus fluorescein angiography may delineate the vascular changes more clearly in this disease.
This occurs when the vasculogenesis fails to move into the next stage of angiogenesis. It is a serious condition and requires prompt treatment.
Reference :
- 1. Committee for the Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity. An International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984;102:1130-1134
- 2. ICROP Committee for Classification of Late Stages ROP. An international classification of retinopathy of prematurity, II: the classification of retinal detachment. Arch Ophthalmol. 1987;105:906-912
- 3. International Committee for the Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity. The International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity revisited. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005 Jul;123(7):991-9
- 4. Cryotherapy for Retinopathy of Prematurity Cooperative Group. The natural ocular outcome of premature birth and retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1994;112:903-912
- 5. Computer-Based Image Analysis for Plus Disease Diagnosis in Retinopathy of Prematurity: Performance of the "i-ROP" System and Image Features Associated With Expert Diagnosis. Ataer-Cansizoglu E, Bolon-Canedo V, Campbell JP, Bozkurt A, Erdogmus D, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Patel S, Jonas K, Chan RV, Ostmo S, Chiang MF; i-ROP Research Consortium. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2015 Nov 30;4(6):5
- 6. Temkar S, Azad SV, Chawla R, Damodaran S, Garg G, Regani H, Nawazish S, Raj N, Venkatraman V. Ultra-widefield fundus fluorescein angiography in pediatric retinal vascular diseases. Indian J Ophthalmol 2019;67:788-94